Introduction
A battery is used in almost all aspects of the modern world,such as remote control and wireless sensors, smart medical devices, and electric cars. Out of the numerous types of battery chemistry that are available nowadays, two types of battery chemistry are the most popular in the home and industries sectors: alkaline and lithium batteries.
On the face of it, the two types of batteries might appear to be alike. However, it is very different inside, in terms of their electrochemistry, performance, cost, and shelf life. It is imperative to understand such variations whether using common day devices or life-time machines that consume 24/7.
Here is a guide that will assist you in choosing the right battery that works best based on the topic you are discussing and enable us to dispel the major differences between lithium and alkaline batteries, the pros and cons of the two batteries and guide you to make informed decisions as of which type of battery is more suitable.
What Are Alkaline Batteries?
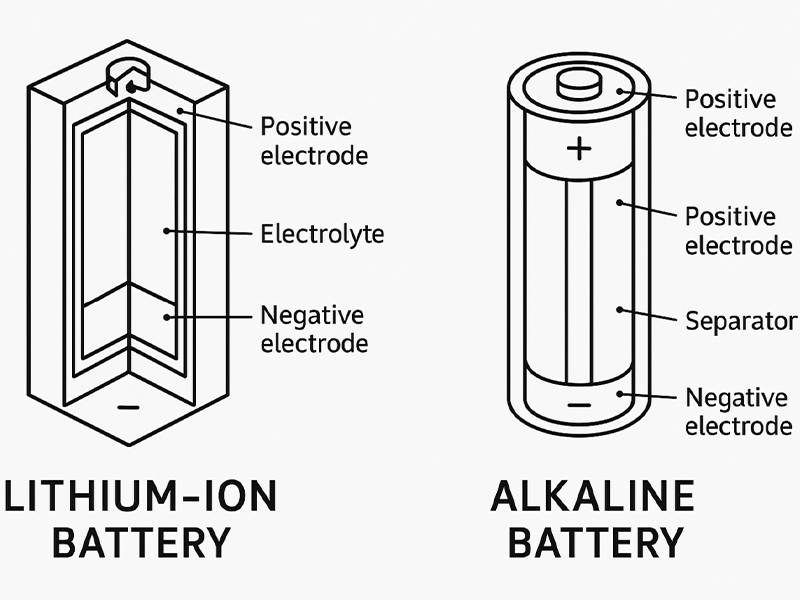
Alkaline batteries are primary (non-rechargeable) cells which use both the zinc and manganese dioxide as electrodes. Electrolyte in is a potassium hydroxide and is alkaline in nature, this allows a constant flow of ions, and it can make the battery give out a consistent voltage during its service lifetime.
The wider use of these batteries as the power source of domestic gadgets such as the clock, flashlights, toys, and remotes controls is common. Catering to the low to middle power requirements, they are cheap and convenient to use daily.
Key Characteristics of Alkaline Batteries:
- Electrolyte: Alkaline potassium hydroxide
- Voltage: 1.5 V per cell
- Shelf life: 5–10 years
- Operating temperature: 0 °C to 50 °C (Normal)
- Common use: Low-drain device
Due to their low cost and high supply, alkaline batteries have continued to be the solution of preference to customers across the globe.
What Are Lithium Batteries?
Lithium batteries have lithium metal or lithium compounds as anode, which provides them with a high energy density and a longer lifespan than alkaline cells. The lithium cells, in contrast to the alkaline batteries, can operate under high drain loads that is, produce consistent power even when the gadgets are demanding regular or peak power.
Depending on the design, lithium batteries can be:
- Primary (non-rechargeable): Often used in cameras, sensors, or pacemakers.
- Secondary (rechargeable, i.e., lithium-ion): Used in laptops, phones, and electric vehicles.
Key Characteristics of Lithium Batteries:
- Electrolyte: Lithium salt in organic solventor solid electrolyte
- Voltage: 1.8 – 3.7 V per cell (depending on chemistry)
- Shelf life: 10–15 years
- Operating temperature: -40 °C to 60 °C (varying)
- Applications: High-drainand critical applications
Lithium batteries are less heavy, stronger and their shelf life is by far longer. This renders them professional and industrial aptitude where the performance cannot be compromised.
Key Differences between Lithium and Alkaline Batteries:
To understand these two battery types clearly, here’s a side-by-side comparison of their most important characteristics:
Table No: 1
| Feature | Lithium Battery | Alkaline Battery |
| Electrolyte | Lithium salt (organic/solid) | Potassium hydroxide (alkaline) |
| Voltage per Cell | 1.8 – 3.7 V | 1.5 V |
| Energy Density | High | Moderate |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Temperature Tolerance | Perform well in extreme cold & heat | Limited temperature extremes |
| Shelf Life | 10–15 years | 5–10 years |
| Cost | Higher | Low |
| Performance in High-Drain Devices | Excellent | Moderate to weak |
| Common Use | Cameras, sensors, EVs, medical | Toys, remotes, flashlights |
Figure 1 Structure of Batteries
This table explains why lithium batteries are commonly preferred in high performance or the critical use case, whereas alkaline batteries are the most cost-effective option where the battery is used by the household on a more frequent basis.
Advantages of Lithium Batteries:
- High Energy Density:
The lithium batteries are much larger than alkaline cells into which the same amount of energy can be stored at a lower size. This implies that the operation period is extended, and the replacements are minimal. - Excellent Performance in Extreme Environments:
They are stable even during freezing or high heat situations and hence can be used in the outdoor and industry segment. - Lightweight and Compact:
Their lightness is an asset when it comes to portables such as GPS trackers, drones as well as medical items. - Long Shelf Life:
The lithium batteries have a shelf life lasting up to 15 years thus making them dependable in emergency backup systems. - Consistent Voltage Delivery:
Lithium cells also provide constant power near the point of exhaustion, unlike alkaline batteries, which are constantly losing purpose.
Advantages of Alkaline Batteries
Figure 3 Pros of Alkaline
- Affordable and Accessible:
The alkaline batteries are cheap and can be found in most stores across the globe. - Safe and Stable Chemistry:
The chances of overheating and short-circuiting are low; thus, they can be used daily. - Ideal for Low-Drain Devices:
Fits well in clocks, remotes, toys, etc. that do not need heavy current. - Decent Shelf Life:
This is shorter than that of lithium though, 5-10 years is sufficient in most consumer applications.
Environmentally Manageable:
Several other places find it simple to dispose of and recycle alkaline batteries as compared to lithium.
Limitations of Both Battery Types:
Lithium Battery Limitations:
- Higher Cost:Lithium batteries are more expensive to manufacture and purchase.
- Special Disposal Requirements:Due to their chemistry, Some types should be recycled appropriately to prevent harm to the environment.
- Overpowered for Low-Drain Devices:Using lithium where it’s not needed can be unnecessarily costly.
Alkaline Battery Limitations:
- Limited High-Drain Performance:Under heavy load voltages will tend to drop resulting in reduced run time of power-hungry appliances.
- Non-Rechargeable:Most of the alkaline batteries do not have the ability to be reused.
- Lower Temperature Tolerance:It plays the game with its body temperature greatly down when hot or when it is too cold.
Applications and Use Cases:
The proper battery will depend on the nature of the device and power consumption:
- Common Applications of Lithium Batteries:
- Digital cameras and flash units
- GPS trackers and drones
- Smart sensors and wearables
- Pacemakers and medical monitoring devices
- Electric vehicles and power tools
- Common Applications of Alkaline Batteries:
- Clocks, radios, and toys
- Remote controls and flashlights
- Wireless computer peripherals
- Smoke detectors
- Simple emergency lighting
Pro Tip: Lithium batteries are best for devices that run continuously. Alkaline is appropriate for application in the cases of low and intermittent energy demand.
Which Battery Should You Choose?
Table No: 2
| If You Need… | Choose Lithium | Choose Alkaline |
| High performance | Yes | No |
| Low cost | No | Yes |
| Long shelf life | Yes | Yes |
| Extreme temperature operation | Yes | No |
| Everyday household use | No | Yes |
| High-drain application | Yes | No |
Lithium is the better choice when performance, reliability, and lifespan are priorities.
Alkaline is the practical option when cost and availability matter more than performance.
Future Insights:
With the continuous development of energy storage technology, it is very likely that lithium batteries will dominate the high-performance markets such as Electric Mobility, Smart Grids and Portable electronics. Manufacturers are also trying to improve recycling lithium and to make these batteries cheaper so that they can be used in everyday life.
The alkaline batteries, however, do not dispose of themselves. Their low cost, chemical predictability and convenience of availability will mean that they will remain in use for low draining applications by households and businesses for many more years.
Hybrid energy systems will likely hit the market within the next 10 years where lithium and alkaline batteries will in fact co-exist and fulfill their next-generation role rather successfully.
Check out our High-Performance Battery Testing Solutions to find out how the right battery technology can help boost your energy strategy.
Key Takeaways:
- Lithium batteries deliver higher performance, last longer, and handle extreme conditions better.
- Alkaline batteries are cost-effective, easy to find, and great for low-power devices.
- The right choice depends on your use case, not just price.
- As technology evolves, lithium is expected to take a bigger role, while alkaline remains essential for everyday use.
FAQs:
1.Is it possible to substitute the lithium batteries with the alkaline batteries in any equipment?
Yes in most cases but only when the voltage and the size are compatible. Lithium batteries are great substitutes in high-drain equipment, although it is important to consult with recommendations of the device manufacturer to prevent damage.
2.Are the batteries rechargeable lithium?
Not all. The first type of lithium battery is non rechargeable, which is called primary lithium batteries, whereas these secondary lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable ones found in most modern electronics such as smart phones and power tools. Always look at the label prior to charging.
3.Can it be stated that lithium batteries can be used in domestic appliances?
Yes, and they are safe, usually, when properly used. Lithium batteries are well-protected and less likely to leak as compared to alkaline batteries. Never expose them to too much heat, seek out puncturing and mixing them with other types of batteries though.
4.Is it possible to combine lithium and alkaline batteries?
No. Combinations of battery may result in leakage, short circuiting, or disproportionate discharge. Always ensure that you use the same type and brand of battery in the same device to achieve maximum safety and performance.
5.What kind of battery will work in cold conditions better?
The lithium batteries are much stronger during extreme heat and cold. Alkaline batteries are known to drop Voltages or lose capacity at low temperatures.
6.Why are lithium batteries costly as compared to alkaline?
Lithium batteries are made of highly developed materials, have increased shelf life and they are more effective. These advantages have greater manufacturing expenses hence they are costly in the short term but more economical in the long term.
7.Are alkaline batteries more likely to leak in comparison with lithium batteries?
Yes. Alkaline batteries leak more particularly when left in devices over a long period or completely discharged. Lithium batteries have more robust seals and stability and therefore, the leakage is less frequent.
8.What are the safe ways of disposing lithium and alkaline batteries?
Lithium batteries are to be brought to licensed recycling. In some areas, alkaline batteries may be put in household waste, although recycling is always better, although in some areas, they are not allowed. Disposal Do not deposit batteries in fire or the trash bins.
9.What is the best battery to use in daily applications in remotes, toys and clocks?
In low-drain devices, the alkaline batteries are economical and operate well. Lithium batteries are suited better to devices that require longer working time or their extreme usage. It should be based on power demand and requirements of the environment.
Ready to optimize your battery testing process?
Explore our full range of Battery Test Systems including EV, module, and high-voltage solutions to ensure reliability and efficiency in every test.