Introduction
One of the most popular and widely used power sources in the world, AA batteries can be found powering everything from remote controls to wireless mice, flashlights, toys, cameras and more. But AA cells come in several varieties, especially when it comes to voltage, chemistry and recharge ability, something which few people really understand. These differences have practical consequences on how you use your AA cells. This article aims to provide some basic ideas about the various lithium AA battery types: their voltage ratings as well as common measurements and applications of each type.
Figure 1: Lithium AA Batteries
Understanding the Voltage of AA Batteries
Before exploring the different types of AA batteries, it’s important to understand how voltage works and why it matters.
The voltage of an AA battery depends on its chemistry. Although all AA batteries have the same physical size, the materials and chemical reactions inside determine how much electrical energy each type can provide. To ensure voltage stability and performance validation, check out our Battery Test Systems designed for laboratory and industrial applications.
Table 1: Standard Voltage Ranges
| Battery Type | Chemistry | Nominal Voltage | Rechargeable | Common Use |
| Alkaline AA | Zn–MnO₂ | 1.5 V | No | Clocks, remotes, toys |
| NiMH AA | Nickel–Metal Hydride | 1.2 V | Yes | Cameras, wireless devices |
| Lithium (Primary) AA | Li–FeS₂ | 1.5 V | No | Outdoor & cold-weather gear |
| Lithium-Ion AA | Li-ion | 3.6–3.7 V (regulated 1.5 V) | Yes | High-drain electronics |
Why Voltage Matters
The pressure can be delivered by the battery the voltage is determined how high Devices which are intended for 1.5 V batteries will be wrong or even get damaged under high voltage. So things like ,if too as battery the device may perform erratically or even shut off prematurely. For instance, a simple flashlight designed for 1.5 V used an unregulated 3.7 V lithium-ion cell could destroy its LED or inside elements. Also, therefore knowing the voltage rating of your AA battery is not just a matter for technical trivia it’s essential to fit together and secure equipment.
Types of AA Battery
Now that the role of voltage is clear, let’s examine the most common AA battery types and their characteristics.
Table 2: Common Types of AA Batteries
| Type | Chemistry | Nominal Voltage (V) | Rechargeable |
| Alkaline AA | Zinc–Manganese Dioxide (Zn–MnO₂) | 1.5 | No |
| NiMH AA | Nickel–Metal Hydride | 1.2 | Yes |
| Lithium (Primary) AA | Lithium–Iron Disulfide (Li–FeS₂) | 1.5 | No |
| Lithium-Ion AA | Lithium-Ion (LiCoO₂ / LiFePO₄) | 3.6–3.7 (often regulated to 1.5) | Yes |
| NiCd AA | Nickel–Cadmium | 1.2 | Yes |
| NiZn AA | Nickel–Zinc | 1.6 | Yes |
| Typical Capacity (mAh) | Advantages | Limitations | Common Applications |
| 2000–3000 | Inexpensive, widely available, long shelf life | Not suitable for high-drain devices, not rechargeable | Clocks, remotes, toys |
| 1500–2800 | Rechargeable, good high-drain performance, eco-friendly | Loses charge over time (self-discharge) | Cameras, game controllers, flashlights |
| 3000–3500 | High energy density, long shelf life, performs well in cold | More expensive, non-rechargeable | Outdoor gear, digital cameras, sensors |
| 2500–3500 (regulated output) | Rechargeable, high capacity, stable output | Requires specific charger, higher cost | High-performance electronics, flash units |
| 600–1000 | Durable, tolerates high current | Memory effect, toxic cadmium, obsolete | Industrial and legacy devices |
| 1500–2000 | Higher voltage, good power output | Shorter lifespan, limited availability | Flashlights, cameras, tools |
Physical Dimensions of AA Batteries
Its internal differences are although all AA batteries are designed to one universal size standard. Length: 50.5 mm (1.99 inches), Diameter: 14.5 mm (0.57 inches) The IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) states these consistent dimensions allow use with hundreds of electronic devices simultaneously. Perhaps because of built-in safety circuitry elements, several types of rechargeable cells are a bit longer! This tiny lengthening effect may cause them to jam municipal battery racks as well.
Are All Lithium Batteries Rechargeable?
One common misinterpretation is that all batteries made from lithium are rechargeable. However, this is not true.
- Primary lithium batteries are not to be recharged. Unless of course you want leaks or even explosions.
- A lithium-ion battery recharges and discharges by means of reversible chemical changes.
This is why all lithium batteries have roughly the same chemistry; but it is only lithium-ion or lithium-polymer types that can be recharged.
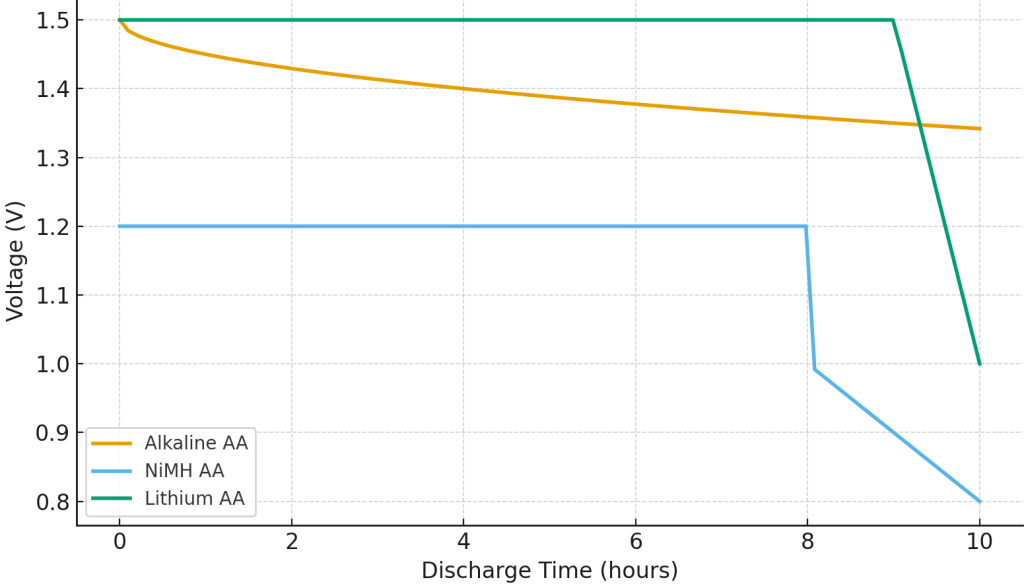
Lifespan and Performance of Rechargeable AA Batteries
Apart from their voltage differences, rechargeable AA batteries vary greatly in performance and lifespan.“How long do rechargeable AA batteries last?” has two answers one for runtime per charge and another for overall lifespan shown in Table 3.
Table 3: Lifecycle and Performance analysis of AA Batteries
| Battery Type | Chemistry | Nominal Voltage (V) | Typical Capacity (mAh) | Recharge Cycles |
| NiMH AA | Nickel–Metal Hydride | 1.2 | 1500–2800 | 500–1000 |
| Low Self-Discharge NiMH (LSD NiMH) | Improved NiMH | 1.2 | 1900–2500 | 700–1200 |
| Lithium-Ion AA | Li-ion (regulated 1.5V) | 3.6–3.7 (regulated 1.5) | 2500–3500 | 300–500 |
| NiCd AA | Nickel–Cadmium | 1.2 | 600–1000 | 700–1000 |
| NiZn AA | Nickel–Zinc | 1.6 | 1500–2000 | 300–500 |
| Self-Discharge Rate | Runtime per Charge | Storage Life | Key Features |
| Moderate (10–20%/month) | Medium (depends on load) | 3–5 years | Eco-friendly, widely available, consistent output |
| Low (1–3%/month) | Long (holds 85% charge after 1 year) | 5–7 years | Excellent balance between longevity and performance |
| Very Low (<2%/month) | Long | 5–10 years | High energy density, lightweight, steady voltage output |
| High (20–30%/month) | Medium | 2–3 years | Durable under heavy load but suffers from memory effect |
| Moderate | Short to Medium | 3–4 years | Higher voltage for demanding devices, shorter lifespan |
Figure 2: Discharge Profiles of AA Batteries.
Application Guide: Choosing the Right AA Battery
After understanding all the major AA types, the next step is choosing the right one for your device. For professional testing and validation of AA battery performance, explore our Battery Test Systems.
Table 4: Choosing an Appropriate AA Battery
| Device Type | Recommended Battery | Reason |
| TV Remote, Clock | Alkaline AA | Low drain, long shelf life |
| Flashlight (emergency) | Lithium primary AA | Excellent in cold, long storage life |
| Wireless Mouse/Keyboard | NiMH rechargeable | Reusable, stable voltage |
| Digital Camera, Toy Drone | Lithium-ion AA | High capacity, handles high current |
| Sensor or IoT Device | Lithium AA (primary) | Long life, low self-discharge |
Safety Note: Before replacing a 1.5 V cell with a 3.7 V cell, always check your device’s voltage requirements. Some compatible devices can safely use batteries with a soldering point at the base.
Conclusion
Overall, AA batteries may look identical, but their internal chemistry defines their true capabilities. But inside, they differ significantly in voltage, capacity and how they perform. For everyday consumer electronics low drain devices alkaline batteries are still the first choice; while NiMH or lithium ion rechargeable has long since been a no-brain high drain and environmental problem.Understanding these differences helps you achieve better performance and device safety.
FAQs
Q: What is the voltage level of a AA battery?
A: The voltage of a standard AA battery is about 1.5 volts.
Q: What is the voltage of a AA Alkaline battery?
A: Depending on the state of charge. Its usual terminal voltage is about 1.5V with a fresh charge, but as it discharges this will drop slowly for instance down to 1.3 V when fifty percent used up.
Q: What are the measurements of a AA battery?
A: About 50.5 mm in length and 14.5 mm in width.
Q: What is the total number of times rechargeable batteries can be used before they become ineffective?
A: Between 500 and 1000 charging cycles.
Q: Do all lithium batteries support recharging?
A: No. Certain lithium batteries are designed for single use.