The transportation industry is undergoing a major transformation driven by electric vehicles (EVs), enabled by high-energy-density batteries, low emissions, and advanced control technologies. However, safety consideration, especially thermal runaways, is a critical phenomenon and a self-accelerating process that can lead to overheating, fire, or even explosion if no proper precautions are taken.
In this article, the importance of thermal runaway in EVs, why it occurs, practical incidents of thermal runaway and how modern EV design and best practices are required to prevent it.
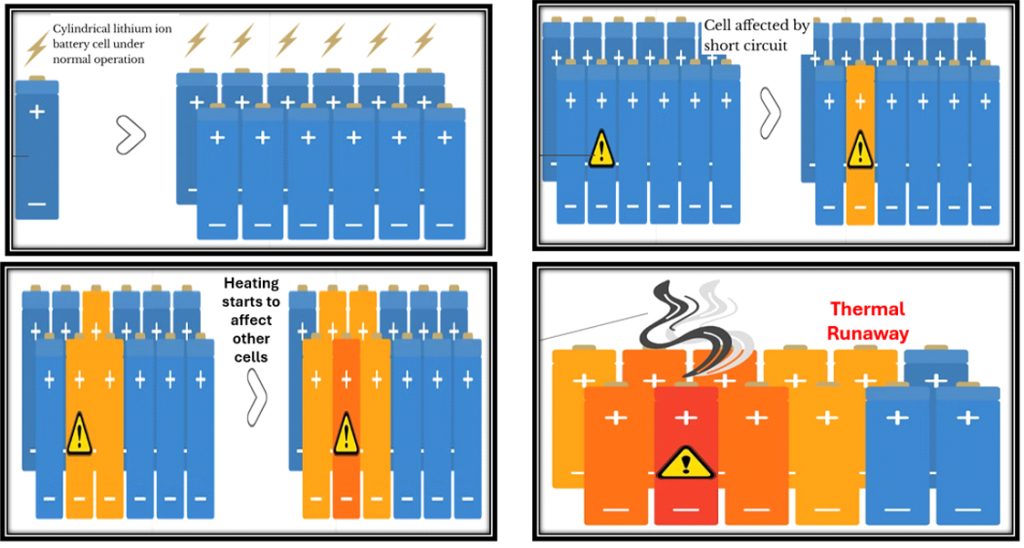
What Is Thermal Runaway?
Thermal runaway is a reactive chain reaction within a cell of a battery where the heat production is higher than the heat loss. After being triggered, internal temperature runs out of control, increasing the rate of chemical reactions and generating even higher temperatures. This escalating process leads to cell rupture, fire and explosions if not stopped earlier.
Key Causes of Thermal Runaway of EV Batteries
Thermal runway in EV batteries do not occur suddenly or without reason. It is usually the result of one or more internal or external stress factors that disturb thermal and electrochemical balance of lithium-ion cells. Understanding these causes is essential for designing safer battery systems and implementing effective preventive strategies. Some of the key causes are as follows.
Internal Short Circuits:
The internal short circuit occurs when a direct current flows inside a battery cell. The positive and negative electrodes inside a battery cell come into direct contact during short circuit. As a result, intense heat is produced that triggers the runaway process. The short circuit happens due to defects in manufacturing, or micromaterials impurities, or damage to the isolator between electrodes.
Overcharging
The operation of battery beyond its safe voltage and current limits or overcharging. The excessive voltage and current produces heat instead of stored energy. Overcharging can lead to:
- Decomposition of the electrolyte
- Breakdown of electrode materials
- Release of oxygen from the cathode, which fuels combustion
Similarly, high rate charging or discharging (electrical abuse) increases internal resistance losses. These internal losses produce heat, and must manage it properly. without battery cell comes into an unstable thermal state, triggering runaway reactions.
High Operating Temperatures
Temperature is directly associated with heat and EV batteries are highly sensitive to temperature. The risk of thermal runaway increases when batteries operate at high temperature. As a result, High temperatures have following impact:
- Accelerate chemical reaction rates inside the cell
- Degrade the electrolyte and electrode materials
- Reduce separator mechanical strength
The main cause of thermal runaway of EV batteries is high operating temperature due to poor thermal management, hot climates or constant high-power consumption.
Battery Aging and Degradation
The cell of EV batteries gradually deteriorates, and the chance of thermal runaway increases in this situation. Aging effects include following:
- Increased internal resistance, leading to higher heat generation
- Loss of electrolyte stability
- Formation of micro-cracks in electrodes
- Reduced heat tolerance of internal components
Even during normal operation, older cells are more vulnerable to stress conditions
Prevention and Safety Measures
To restrain thermal runaways in the EV, a multi-layer safety approach is adopted globally. The best practices for prevention and safety measures are as follows.
Battery Management Systems (BMS)
A BMS is most critical prevention technology to minimize thermal runaway. Modern BMS architecture continuously monitors following:
- Cell voltage and current
- Cell and module temperature
- State of charge
- State of health
BMS monitors critical parameters (overvoltage, undervoltage, overcurrent and high rate of temperature increase) to minimize thermal runaway. Following corrective measures are taken such as:
- Reduction of charge or discharge rates
- Isolating faulty cells or modules from healthy cells
- Shutting down the battery system entirely in extreme conditions
A BMS maintains a continuous check of all above-mentioned parameters (cell voltage, current as well as temperature) to maintain safe operating conditions. It balances charging the cell and can shut down systems in case abnormal behavior.
Thermal Control and Cooling
It is utmost critical to maintain battery temperature within a safe operating range. EVs employ advanced thermal management systems (TMS) such as:
- Liquid cooling systems for uniform heat removal
- Heat spreaders and thermal interface materials to eliminate hotspots
DC Fast Chargers (Level 3), high-power acceleration, or regenerative braking also generate heat, but TMS dissipate that heat efficiently to prevent localized overheating that trigger runaway reactions.
Prevention of Thermal Propagation
The failure of single cells is unavoidable even with preventive measures. Controlling thermal propagation is critical. Following steps are necessary to lower the chances of a chain reaction that would cause the thermal runaway.
- Fire-resistant insulation between cells and modules
- Use of ceramic coated separators
Safe Charging Infrastructure and Practices
Charging conditions directly influence battery safety. The fast charger (Level 3 Type) can cause thermal runway due to fast charging. Preventive practices involve:
- Using certified chargers compatible with battery specifications
- Implementing controlled charging profiles, especially during fast charging
- Avoiding charging at extreme temperatures
- Integrating vehicle-to-charger communication to regulate power flow
Conclusion
From an industry perspective, advanced battery testing, thermal validation, and safety certification play a critical role in identifying early thermal risks and improving EV battery reliability. You can learn about the top 10 battery testing equipment brands. Excessive heat in a battery leads to the condition of thermal runaway, however, present-day electric vehicles will avoid this phenomenon by providing smart monitoring, adequate cooling, and powerful protective designs. High-tech battery systems monitor any issues and take early action to ensure safe operation of batteries. Practical measures (like charging with correct chargers and no extreme temperature conditions) to end users also reduce the risk of thermal runaway. With the rise in technology and safety standards, EV batteries are becoming safer, reliable and can be applied in ordinary life.