Introduction
A 12V battery is an electrochemical storage device containing chemical energy and provides electrical power for various DC devices. It is predominantly used in automotive applications, machines, marine systems, and renewable energy storage. It is valued for its reliability, rechargeability, and cost–energy density compromise.
12V batteries also promote environmental sustainability by enabling renewable energy storage, reducing carbon emissions, and supporting resource efficiency by being recyclable and having second-life uses. They are also central to pushing greener and cleaner energy systems.
Figure 1: Sustainable Batteries for a Sustainable World
Structure and Working Principle of a 12V Battery
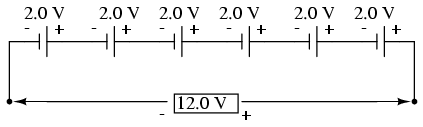
An ordinary 12V battery is in fact six electrochemical cells in series, which give about 2.0–2.1 volts each. The combined voltage under load (when applied a charge) typically runs at about 12.6-12.8 volts compared to a discharged battery which should read around 11.8 or so while unloaded and not charged up. The electrodes (positive and negative plates) are held in an electrolyte into which they are immersed in each cell. For lead-acid accumulators the electrolyte is sulfuric acid and for lithium-ion accumulators a solution of lithium salt in an organic solvent.
Chemical reactions occur at the electrodes upon discharge of the battery, and electrons are liberated which flow through an external circuit to power applications. Simultaneously, ions in the electrolyte are transported to neutralize the charge. When charging, the outside voltage acts in reverse and undoes these reactions to bring the chemical potential of the battery back up. This reversible electro-chemical reaction is what allows for the 12V rechargeable batteries to have multiple charge and discharge cycles over many years.
Figure 2: Internal Structure of a 12V Battery, six 2V cells connected in series.
Types of 12V Batteries
There are several types of 12V battery chemistries… each can be tested and characterized with SINEXCEL-RE Battery Test Systems to evaluate performance consistency.
- Flooded Lead Acid (FLA):The original, and still most common. They are filled with a liquid sulfuric acid electrolyte, and need maintenance such as topping up water. They are cheap, but clumsy and spill electrolyte.
- Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM):A type of sealed lead‐acid battery in which the electrolyte is absorbed within a fiberglass mat. AGM batteries are a maintenance free, non-spillable and provide more cranking power as they’re predominantly used for starting vehicles with modern accessories.
- Gel Cell:Different type of sealed lead-acid design in which the electrolyte is a gel. Gel deep cycle batteries have much better wear and tear on the battery during heavy discharging and vibration which is usually associated with marine, solar power system etc.
- Lithium-Ion (Li-ion):These batteries are charged with lithium-based chemistries (for example, LiFePO₄) and generally show higher energy density, lower weight, longer cycle life and better charge efficiency than lead-acid batteries. They are being used more and more in renewable energy storage and electric cars.
- Nickel-based (NiCd, NiMH):For 12V products, nickel-cadmium and metal hydride batteries are used in specialized military and industrial applications where robustness and wide temperature range are needed.
Applications of 12V Batteries
The 12-volt batteries are used in many different applications because of their versatility:
- Automobiles:12V batteries are predominantly used in cars to start the engine, power the lights, audio system and other electronic devices present in car dashboard. Even electric cars are often equipped with some kind of 12V auxiliary battery to power such low-voltage systems.
- Solar And Wind Energy Storage Systems:The most suitable application for 12V batteries, which can often be found in off-grid and hybrid power systems. They charge when generation is high (and prices are low) and discharge, typically on the 15-minute market, when demand or other factors are such that generation costs more than regulation service.
- UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply):12 volts batteries are crucial parts of the UPS’s that defend sensitive electronic equipment’s in case of power failures. They offer battery backup that maintains network connectivity during a power outage.
- Portable and Specialized Equipment:From emergency spot lights to camping equipment to home medical devices, 12V batteries can be used as the back-up power supply for these applications. They are available in a variety of voltages for easy implementation into most system designs.
Advantages of 12V Batteries
- Standardized Voltage:Compatible with most DC applications, for use without the hassle of changing voltage.
- Widely Available:They are commercially available in abundance, cost effective and accessible in a variety of chemistries and capacities.
- Reliable:12v lead-acid batteries can be used for decades in critical applications.
- Scalable:Multiple 12V batteries can be wired in series or parallel to get higher voltage or arrange larger capacity, it’s flexible for small and large requirement.
Limitations of 12V Batteries
- Weight and Bulk:Lead-acid types are heavy, which makes it impractical for use on the move.
- Cycle Life:For a flooded lead-acid battery, there is the average maximum of about 500–1000 cycles before noticeable degradation—much less than lithium-ion options.
- Extreme Temperature Performance:Cold temperatures significantly reduces the capacity of 12V batteries, and hot weather heats them up causing internal damage.
- Voltage Drop:Even though 12V batteries discharge to near-zero voltage the advertised size of this battery is rated at an “unrealistic” Voltage (20hr rate).
How Long Will a 12V Battery Last?
Based on chemistry (user pattern and environment), the life of a 12V battery can be extremely different. Most lead acid batteries can last for 3-5 years with 500-1000 charge-discharge cycles. Various sealed AGM and gel types are more durable, lasting 4–7 years. The 12V lithium ion batteries are the most long lasting that is available until now of around 8–12 years life with cycle count around (2000-5000). However, the lifetime of the battery depends on its use frequent deep discharges, overcharging or exposure to high temperature will accelerate ageing and shorten life.
Table 1: Lifespan of 12V Batteries
| Battery Type | Typical Lifespan | Cycle Life (Approx.) |
| Lead-Acid | 3–5 years | 500–1000 cycles |
| AGM / Gel | 4–7 years | 700–1500 cycles |
| Lithium-Ion | 8–12 years | 2000–5000 cycles |
Maintenance and Care
Regular maintenance will greatly prolong the life of a 12V battery. Wet cell lead-acid batteries need occasional watering and terminal cleaning. Sealed types such as AGM and gel are maintenance free, but they also require proper charging. A lithium-ion battery is a protected battery, but there are unprotected batteries that do not have any protection circuitry at all so they rely on hardware to monitor and control voltage ranges, heating limits and cut-off charging/cut off discharging.
Best practice in general are to avoid deep discharges, use smart chargers with overcharge protection, have good ventilation, and store cells in a cool dry place. Occasional (periodic) testing of underwater loader battery can, however, ensure that the condition of the battery is known and failure during operation is avoided.
Charging of 12V Batteries
Charging methods directly affect battery life — using a battery testing system helps simulate and record real charge/discharge cycles safely.Will affect the battery life. The proper charge profile of a lead-acid battery is typically thought to be performed in three stages (bulk, absorption and float) with voltage limits to prevent gassing and water loss. Li-ion batteries necessitate a constant current, constant voltage (CC/CV) charging operation and have to be cut off at specific voltages by a BMS. Both chemistries degrade faster at an overcharge condition, deep discharge and high temperature.
Modern Developments and Trends
There’s been a new movement in recent battery development that has actually pushed 12V systems to do even more now. Although higher-voltage battery packs take centre stage in electric vehicles, their little sibling, the auxiliary 12V battery, is still of critical importance. Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO₄) 12-V batteries are many renewable energy systems standard for their safety, stability and longevity. And should 12V not be enough for your high consumption appliances, rest assured they can also easily be connected in series or parallel to form 24V, 48V.
Environmental and Green Benefits of 12V Batteries
12V batteries bring significant environmental and sustainable advantages. They are readily recycled, with up to 95–99% recoverability of raw materials while eliminating virgin material extraction and waste. They can also support renewable energy infrastructure, such as solar and wind systems, by storing excess energy and reducing dependence on fossil fuels while decreasing greenhouse gas emissions. With long lifespans (especially in the AGM & gel types) they minimize disposals and could potentially be used as second life storages. They also improve the energy-efficiency in off-grid systems as well as reduce CO2 emissions when incorporated into hybrid and electric vehicles. Current 12V batteries are environmentally friendly with easy to dispose, safe solution disposal.
Figure 3: Global Regulations for Sustainable Battery Recycling
Table 2: Environmental and Sustainable Advantages of 12V Batteries
| Advantage | Description | Environmental Impact |
| Recyclability | Up to 95–99% of lead and plastics can be recovered and reused | Reduces raw material extraction and landfill waste |
| Support for Renewable Energy | Used in solar, wind, and other renewable systems for energy storage | Decreases reliance on fossil fuels, lowers GHG emissions |
| Energy Efficiency in Off-Grid Use | Reduces energy losses in transmission and distribution | Minimizes carbon footprint and enhances local energy access |
| Long Lifecycle and Second Life | AGM and gel batteries last 4–6 years, can be reused in low-demand applications | Delays waste generation, maximizes resource utilization |
| Reduced Carbon Emissions | Enables hybrid/electric vehicle energy systems and small-scale energy storage | Lowers greenhouse gas emissions and fuel consumption |
| Environmental Compliance | Meets RoHS, REACH, and other regulations | Ensures safe handling of hazardous materials |
Conclusion
The 12V battery, today’s energy ecosystem universal and essential. Its uses span starting car engines to storing renewable energy and powering critical backup systems. From a choice of inexpensive lead-acid and high-performance lithium-ion to the best value in cost per cycle, batteries offer the right choice for various applications concerning cost, cycle life, weight or efficiency. Transparency into their construction, usage, uses and upkeep is what ensures 12V batteries provide the ultimate levels of reliability and life extension, to make it a timeless technology for decades-old power sources, as well as more modern ones.
For professionals developing or validating battery systems, explore SINEXCEL-RE Battery Testing Solutions — designed for precision, scalability, and efficiency.
FAQs about 12V Batteries
- What is a 12V battery?
A device that stores energy and supplies 12V DC power.
- Where is it used?
In cars, solar systems, UPS units, and portable devices.
- How long does it last?
About 3–12 years, depending on the type and usage.
- Can it be recharged?
Yes, most 12V batteries are rechargeable.
- Is it eco-friendly?
Yes, it’s recyclable and supports renewable energy.