Solid-state batteries, as the name indicates, are those energy storage devices which have solid electrolytes rather than liquid or gel polymer type electrolyte. Solid electrolyte makes these batteries capable of tolerating higher temperatures and have higher thermal stability. Solid-state batteries have high energy density, longer lifespan , and capability of fast charging. It is also expected that these batteries could help extend EV range beyond 600 miles after a single charge.
Promising features of solid-state batteries have urged scientists and manufacturers to explore this battery type more. Their satisfactory outcome welcomes learners and laymen to know these batteries holistically to get better outcomes.
In this article, we will explore structure and features of solid-state batteries, and know their application areas especially associated with green energy goals. Challenges associated with widespread adoption of solid-state batteries are also discussed. During discussion, we will also establish a comparison guide between solid state batteries and commonly used lithium batteries.
Structure of a Solid-State Battery
Batteries with solid electrolyte and electrodes – also known as all-solid-state batteries have promising structural properties. On the basis of configuration, solid-state batteries are categorized into thin film and bulk-type batteries.
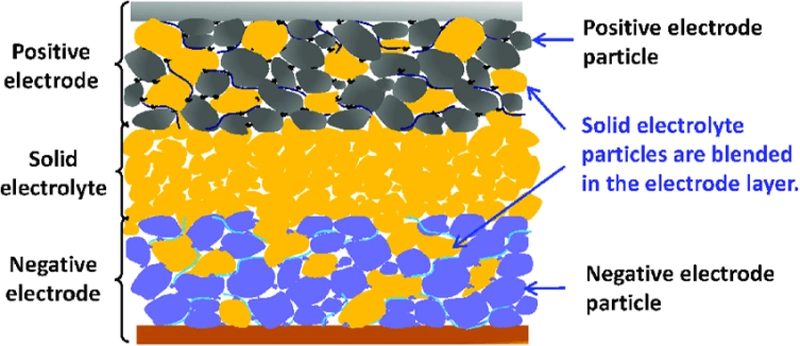
Thin-film solid-state battery consists of solid electrolyte film, and two electrodes – negative and positive. Like traditional batteries, electrolyte is sandwiched between two electrodes.
Bulk-type solid-state batteries have composite electrodes containing solid electrolyte particles and an active material. Between two composite electrodes, there resides a solid electrolyte separator. To increase contact area between electrolyte and electrode, and form lithium-ion conduction pathway, electrolyte particles are blended into both electrode layers.
Schematics diagram of a solid-state battery shows internal structure of solid-state batteries for illustration and better understanding. Due to their unique internal structure and material properties, solid-state batteries require specialized testing equipment to evaluate performance, safety, and lifecycle. Advanced 电池测试设备 plays a vital role in accelerating solid-state battery development. One important aspect about the structure of solid-state battery is absence of separator which is of high importance in li-ion and other types of batteries. Absence of separator brings about many features of the battery including high energy density, safety, and design simplicity, and construction feasibility.
Important Features of Solid-State Batteries
Solid state batteries designed with solid type electrolyte have many features which make these batteries an attractive choice for many applications. In this section, we will discuss these features briefly.
高能量密度
Solid-state batteries have high energy density due to multiple reasons. First, presence of solid electrolyte eliminates the need for separator. A component reduced means weight lowered and space saved. Second, safety risks associated with solid-state batteries are lesser than batteries with liquid electrolyte. Due to this, less space is required to incorporate safety specs into its structure. Consequently, weight and volume of final product get further reduced improving energy density. Third, multi-layer cells can be constructed to increase power output as cell weight is low.
Good Temperature Tolerance
Solid electrolytes are more thermally stable than liquid electrolytes. It makes the battery operation comparatively more risk-free. Solid electrolytes are selected to have good ion conduction, so performance doesn’t degrade even at low temperature. In reality, power output of all-solid-state batteries increases further at higher temperatures as solid electrolytes with greater conductivity are used.
In comparison, lithium-ion batteries become safety risk at low temperature and chances of their permanent damage are also enhanced.
To add further, presence of solid electrolyte suppresses side reactions which can contribute to heat production or pose safety threat.
Long Lifespan
Advanced solid-state batteries have lifespan of 10-15 years and can undergo 8000 to 10,000 charge-discharge cycles. Though, initial price of all-solid-state batteries is quite high but longer lifecycle makes them a viable option for demanding applications like that of EVs. In comparison, 锂电池 can endure 1500-2000 cycles on average.
Better Safety Features
All-solid-state batteries are better in terms of safety. Lithium-ion batteries with liquid electrolyte are prone to dendrite growth, short circuiting, explosions, and fire specially when subjected to high current operations at subzero temperature or high temperature. These factors limit usability of li-ion batteries in many settings. Another safety risk associated with li-ion batteries is electrolyte leakage.
On contrary, presence of solid electrolyte in solid-state batteries reduces the risks of electrolyte leakage and dendrite growth. As dendrite growth is halted, prospects associated with short-circuiting and fire are also eliminated.
快速充电
Fast charging is a highly demanded feature for many applications. For example, EVs need fast and safe charging mechanisms and batteries to beat wait-time anxiety, and make EVs more practical option. Solid-state batteries are well-suited in this regard as they can show 80% increase in SoC (State of charge) in less than 10 minutes with three electrode arrangement. Comparatively, solid-state batteries charge almost six times faster than highly adopted lithium ion batteries.
Fast charging can degrade capacity in li-ion batteries, but solid-state batteries have shown promising performance in this regard also. Extensive research and industry experiments have shown that solid-state batteries are retaining up to 81% of their originally rated capacity even after 3000 fast charging cycles.
Application Areas for Solid State Batteries
Solid-state batteries are set to revolutionize many application areas which demand high energy density, enhanced safety, better thermal performance, and fast charging. With increased focus on environmental sustainability, automotive sector is the very first application area needing Solid-State Batteries (SSBs). Demanding features of solid-state batteries make them suitable for many other applications also like medical devices, consumer electronics, IoTs (Internet of Things), and renewable storage. Here, we will be relating different application areas with suitable features of SSBs.
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Fast charging capability, high energy density, and better thermal performance make solid-state batteries a very suitable option for EVs.Fast charging capability, high energy density, and better thermal performance make solid-state batteries a very suitable option for EVs.To ensure safety and reliability of EV battery packs, comprehensive testing solutions are required throughout development and production. Learn more about our EV Battery Testing Equipment.
EVs are mobile devices and their target environment can’t be predicted at the time of manufacturing and assembling. So batteries with wide temperature range tolerance and enhanced safety features are more suitable for EVs.
A major hindrance in the adoption of EVs is long waiting duration for battery charging. Fast charge capability of SSBs resolves these problems and makes these batteries further suitable for EVs.
Consumer Electronics
Trend of light weight and smart devices is increasing with each passing day. Lightweighted SSBs packed with high energy and longer lifespan are very suitable for consumer electronics due to mentioned features.
医疗设备
Medical devices need safe, reliable source of power which would be compact and capable of furnishing high power on demand. Due to appropriate feature, SSBs are used in many medical devices including health monitors, and other portable diagnostic tools.
Renewable Energy Storage
Size of renewable installations is increasing in every country and so is the need for energy storage systems. High energy density, long lifespan, and high reliability of SSBs make these batteries a good option for renewable energy storage.
Challenges Associated with Adoption of Solid-State Batteries
Solid-state battery offers higher energy density, fast charging, good temperature tolerance, and good safety features in multiple settings. Nonetheless, this battery type is not highly adopted as of now. There are some challenges which need to be addressed to make solid-state batteries a viable option at commercial level for a range of applications.
Higher Manufacturing cost
Manufacturing of solid-state battery is costlier than that of lithium-ion battery. Some major reasons associated with this high price are following:
- Supply chain of raw materials needed for SSB is not well established yet
- Manufacturing equipment to make SSB still needs lots of improvement.
- There is lack of facilities to process raw materials and perform specific processes required during manufacturing
- Production facilities including drying rooms, sintering ovens and furnaces, and vacuums are not much. And their establishment demands high initial cost
As production costs for Solid-State batteries is quite high so it is difficult for manufacturers to offer solid-state batteries at low rates. Anyhow, extensive research is undergoing to find alternate raw materials and processes so cost could be reduced overall.
Risk of Dendrite Growth
Dendrite growth was one of the main factors which negatively impacted lithium-ion batteries. Dendrite growth not only reduces life of battery but also poses extreme safety risks. Solid-state batteries were brought forward to combat the challenges associated with li-ion batteries. Though, solid-state batteries are less prone to dendrite growth, yet there are minor chances of dendrite formation which is hindering wide spread adoption of SSB for now.
Challenges Associated with Solid Electrolytes
Solid-state electrolyte are chosen with specific characteristics like high ionic conductivity, low cost, wide electrochemical stability, good processability, and high mechanical robustness. As of now, four families of electrolytes (sulfides, oxides, halides, and polymers) are explored for solid-state batteries. Anyhow, one family doesn’t have all-in-one solution available. Each electrolyte comes with its own strengths and weaknesses.
For example, sulfide-based electrolytes have good conductivity but it is hard to handle them because of their extreme sensitivity to air and moisture making them chemically unstable. On the other hand, oxide-based electrolytes are chemically stable but mechanically brittle. Moreover, they are less conductive and need sintering at very high temperature during manufacturing process.
Non-availability of Recycling Facilities
With development of each product, crucial step is to develop holistic recycling facilities for that product so it could be disposed-off at the end of its lifecycle without creating significant environmental impact. Such recycling facilities are not available for solid state batteries yet because research on cost-effective recycling methods and development of such facilities will take time and dedication by governments, researchers, and industrialists.
Other Challenges
Other challenges towards the mass development and wide spread adoption of solid state batteries include
- Lack of adequate interface stability between electrodes and solid electrolyte
- Brittleness of solid electrolyte
- Electrode design
- Architectural trade-offs
- Safety concerns
结论
Solid state batteries with no liquid electrolyte introduce a promising energy storage technology. With continuous innovation in battery materials and testing methodologies, companies like SINEXCEL-RE are supporting the transition toward safer and more efficient next-generation batteries. Their high energy density, good thermal performance, demanded safety features, fast charge capability, and long life makes them suitable for many applications especially mobile ones. These batteries have high potential in automotive industry, consumer electronics, aerospace industry, renewable storage, medical devices, and IoTs. Anyhow, before their widespread adoption, many challenges need to be addressed through collective efforts of industrialists and researchers.
常见问题:
- What is the lifecycle for Solid-state batteries?
Solid-state batteries have long life span ranging between 8000 and 10,000 charge-discharge cycles.
- Why current EVs don’t have Solid-state batteries despite their numerous benefits?
Solid state batteries have high production cost currently. Moreover, there are many technical challenges related with electrolytes, electrodes, safety etc. That need to be addressed before their mass adoption for EVs.
- Do current solid-state batteries cost more?
Yes, solid state batteries cost more, currently, because technology and supply chains are not mature yet. SSBs cost 4-8 times higher than other battery systems used currently.