Introduction
Any vehicle in use today relies on its own electrical system, and the core of this system is the battery. Modern-day automobiles have 12-volt battery systems, but it was not always the case. 6-volt car batteries, serving an extremely vital role in the development of automotive electrical systems, drove automobiles, motorcycles, and tractors, among other equipment, for decades.
The 12-volt system became standard in the middle of the 20th century, but 6-volt batteries are still used in the restoration of vintage and classic cars, golf carts, and solar energy systems. They have a large deep-cycle capacity, durability, and simple design; hence, they are a viable alternative in most instances.
This paper discusses the basic distinctions between a 6-volt battery and a 12-volt battery, why the auto industry switched to 12-volt, and when a 6-volt system can still be effectively used, and how they differ in terms of power usage in different applications. At the end, you will be in no doubt as to which system is better suited to various requirements and how to get the best out of each system and its life span.To ensure accurate performance evaluation, you can use a battery testing system to measure both 6V and 12V battery efficiency.
Fundamental Differences
A 6-volt battery is made up of 3 lead-acid cells in series to provide a nominal 6.3-volt or so. That is doubled by a 12-volt battery with six cells to supply approximately 12.6-volt. This variation in voltage has a high influence on system design, performance, and applicability.
The following are some Fundamental differences discussed:
Voltage and Current: We can deliver the same power with low current by using a higher voltage level. By using a 12-volt system, we can deliver more power with low current, which will minimize the losses, and thin wires are used, minimizing cost.
Battery Design: Both types of batteries tend to be chemically with lead-acid, but are usually deep cycle, which is designed to be discharged over a longer duration. This raises their popularity in renewable power. High current bursts to power engines are optimized in the 12-volt batteries, especially in automobile use.
Availability and Compatibility: 12-volt batteries are commonplace in the existing automobile market, and therefore, are readily available from specialty stores for old cars and solar systems. 6-volt batteries, however, are not as prevalent but can be found.
Maintenance: Both types are available as flooded, AGM, and gel. Batteries that are flooded need more maintenance compared to AGM and gel, which are usually sealed and have low maintenance.
Table 1 Comparison of a 6V battery with a 12V battery
| Feature | 6-Volt Battery | 12-Volt Battery |
| Nominal voltage | 6.3 V | 12.6 V |
| No. of cells | 3 | 6 |
| Common application | Vintage cars, golf carts, solar | Modern cars, trucks, and most vehicles |
| Starting power | Moderate | High |
| Wiring | Thicker cables needed | Thinner cables suffice |
| Availability | Limited in retail | Widely available |
| Cost | Slightly higher per Ah | More competitive pricing |
| System compatibility | Specific to 6 V systems | Industry standard |
| Maintenance | May require topping up water | Widely available sealed options |
| Conversion | Used in series to reach a higher voltage | Usually, a single unit |
Use Scenarios Comparison
Classic and Vintage Vehicles, Golf Carts: Old classic cars used a 6-volt system till the 1960s. Such vehicles were usually of simple electrical design, and the reduced value was adequate. To the restorers and collectors, it is significant to use a 6-volt battery to ensure that the originality and functionality of these vehicles are preserved. The conversion to 12 volts is possible; however, it needs some modifications in the wiring of the vehicle and its parts.
Modern Vehicles: Virtually all modern passenger cars are run on 12-volt systems. This provides higher efficiency by reducing losses, onboard electronics, and comfort systems. These systems would not require the power of a 6-volt battery.
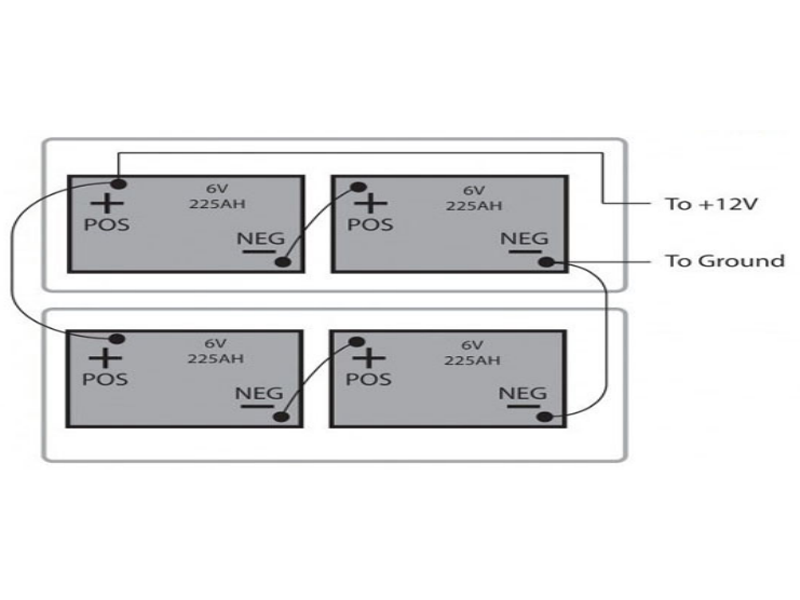
Off-Grid Power and Renewable Energy: Most of the 6-volt deep-cycle batteries used in solar energy applications have long service life and constant discharge properties. The user can create 12-volt or 24-volt banks by connecting two or more 6-volt batteries in series with excellent capacity and duration.
Industrial and Specialty Applications: 6-volt also offers items in the golf cart, forklift, and utility vehicles, where they are easy to maintain and offer consistent power. Industrial engineers often rely on battery module test systems to evaluate performance and ensure safety compliance. Their modularity enables the operators to design the systems as per power needs.
Why Transitioned to 12 Volts
In the mid-1950s, the worldwide automotive sector had moved to 12-volt electrical systems. This trend was not as simple as a trend, but a necessity. With the increased size of engines and the increased number of accessories, the prevailing 6-volt systems could not cope with the demand.
- Power and Performance:The 12-volt system can provide higher power using the same battery AH rating, which is efficient in cold weather conditions where high power is required to start ignition.
- Electrical Load:When the vehicle got new features like radios, air conditioning, and power windows, the power load on the vehicle increased dramatically. A 6-volt system would have been more costly in terms of the cables, and it would have had to use heavier components to carry the same load.
- Efficiency of Wiring:It is possible to reduce the current for the same amount of power by using a higher voltage level. As we know:P=VI. This reduces the voltage drop, allows lighter wiring, and reduces the manufacturing costs.
- Standardization:When the large manufacturers switched to 12-volt systems, the suppliers standardized their products to save money and become more available in the global market.
The Value of 6-Volt in Modern Systems
Despite 12-volt dominance, 6-volt batteries are still a smart choice in several scenarios:
- Vintage and Classic Cars Restoration:
Many vehicles that were produced before the sixties were meant to use 6-volt batteries. The battery should be used correctly to protect the authenticity, or it should not cause over-voltage damage
- Deep-Cycle Energy Systems:
Deep-cycle 6-volt batteries are normally heavier and have thicker plates. When they are configured in series, they are used for variable system voltages for solar, marine, or backup power.
- Golf carts and utility vehicles
Many golf carts and low-speed vehicles conclude that they use multiple 6-volt batteries in sequence that deliver 12-volt or 24-volt.
- Off-Grid Power
A string of 6-volt batteries is very commonly used in RVs, cabins, and remote installations for better power storage that would remain stable and prolonged for a longer period.
How to Choose and Conversion Guide
How to choose a battery between 6V and 12V
| Situation | Recommended Voltage | Reason |
| Vintage or classic car | 6-volt | Preserves authenticity and protects original components |
| Modern vehicle | 12-volt | Standardized system and easy replacement |
| Off-grid or solar storage | 6-volt (in series) | High capacity and flexible system design |
| High cranking applications | 12-volt | Greater starting power |
To convert 6 volts into 12 volts
Other car owners decide to convert old cars into 12-volt cars to achieve improved starting capability and access to parts. This procedure includes changing the generator with a 12-volt alternator, renovating bulbs and ignition parts, rewiring or adding voltage reducers to gauges, and ensuring that the accessories fit in place. It must, however, be properly planned to prevent a blowout on the electrical system of the vehicle. Classic vehicles do not require conversion to 12-volt, and many of the owners do not want to lose historical accuracy and will keep their original 6-volt system.
Maintenance Guide
Batteries should be taken care of to avoid failure in their performance and battery life.
Best Practices:
- Charger should be compatible with the voltage of the battery. Permanent damage will occur when a 12-voltcharger is used to charge a 6-volt
- Maintain terminals clean and non-corroded to have proper conductivity.
- Manifest electrolytes regularly in flooded batteries, pouring distilled water into as much as necessary.
- Deep discharge should not be done unless the battery is built to do so. Overdischarge reduces life expectancy.
- Keep batteries in a dry and cool place when not in use to minimize self-discharge and sulfation.
- Intermittently test the voltage of 6.3 volts using a 6-voltbattery and 12.6 volts using a 12-volt
Buying Advice and Top Brands
When you are buying a 6-volt or 12-volt battery, you should ensure that you have the product that suits your use and performance needs.
Factors to Consider:
- Battery Type: either Flooded, AGM, or gel. AGM/Gel batteries are usually expensive but have the lowest maintenance cost.
- Capacity (Ah) and CCA: Select a capacity that is enough to cover or even surpass the power requirements of your system.
- Warranty and Brand: Well-known brands are more reliable and have longer service life.
- Application: Starting and deep-cycle use.
Leading Global Brands:
- Trojan Battery Company
- Exide Technologies
- Interstate Batteries
- Crown Battery
- Optima Batteries
- Rolls-Surrette
- Duracell
- Varta
- Bosch
Conclusion
The 6-volt battery, even though this technology was invented during the early years of the automotive industry, is a useful and significant source of energy storage in various applications. The rough construction and its deep-cycle capacity enable it to be employed in the restoration of classic cars, off-grid, and specialty equipment.
The 12-volt battery, however, is the worldwide automotive standard as it is more efficient, better in power management, and will fit car systems in the present world.
Whether you use 6-volt or 12-volt systems depends on the application of your application. With knowledge about the technical variations, service requirements, and conversion possibilities, you would make a well-informed choice and guarantee reliable operation for several years.
Both systems find applications in the current energy environment: 6-volt in specialized applications, and 12-volt in mainstream automotive power. They can deliver a solid service life and excellent performance with maintenance.If you need to conduct testing, verification and research and development work, please contact us. We have battery testing systems specially designed for automotive and renewable energy applications.
Common FAQs About 6-Volt Car Batteries
Can we place a 6-volt battery in a 12-volt battery-powered car?
No, a 6 V battery will not be high enough voltage to run a 12-volt system and will probably cause a breakage. You must use the right voltage in accordance with your vehicle.
Will a 6-volt battery be recharged using a 12-volt charger?
No, unless the charger has a 6-volt mode. The battery will be overcharged and damaged by a straight ten-volt charge.
Which car battery has a duration of time that it is sustained on 6-volts?
Normally, 3- 6 years of automotive use. With good maintenance, good quality units can last 7 to 10 years in a deep-cycle solar used application.
Would it be possible to use two 6-volt cells in series so that one can have 12-volt?
Yes, by connecting two 6-volt cells in series, we can get 12-volt. This usually happens with golf carts and solar systems.
The reason behind using 6-volt deep-cycle batteries?
They usually feature heavier plates and can do more discharge cycles than many 12-volt auto starting batteries.
Which vehicles used 6-volt batteries lastly?
Vintage automobiles, antique tractors, motorcycles, and golf carts- a few specialty industry machines.
Will a 12- volt be heavier than a 6-volt battery?
Yes, but two 6-volt batteries connected in series might be required to give the power output of one 12-volt battery. Battery.
Are 6-volt batteries cheaper in comparison to 12-volt batteries?
Not always. Since they are less prevalent, they could be a little higher priced on a per Ah basis.
Is it easy to fit a keener battery so that I can substitute my 6-volt system using a 12-volt?
No, it needs the entire conversion of the electrical (alter Car system, regulator, bulbs, wiring, etc.).
How do I know that I have a faulty battery of 6-volt battery?
Due to battery failure, the engine cranks slowly, examination of lights and voltage reading under 5.8 V shows recovery is poor, and unsuccessful load tests.
Do contemporary automobile designs use any 6-volt systems?
No. Decades ago, passenger cars changed to 12 V. Nonetheless, niche or vintage usage still makes use of 6 V batteries.
Would long durations of storage allow me to store the battery with a voltage of 6-volts?
Yes, but fill it and put it in a dry, cool place, and occasionally refill the charge to prevent sulfation.